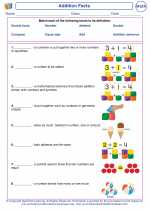
Addition Facts
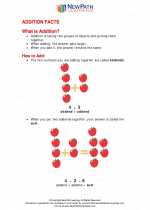
Addition is the process of combining two or more numbers to find their total sum. Addition facts are the basic number combinations that students need to memorize to develop a strong foundation in mathematics. These facts include single-digit addition and are essential for solving more complex math problems in the future.
Examples of Addition Facts
Some common addition facts include:
- 1 + 1 = 2
- 2 + 3 = 5
- 4 + 5 = 9
- 7 + 8 = 15
Importance of Learning Addition Facts
Memorizing addition facts is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation. It helps students develop fluency in mental math, improves problem-solving skills, and lays the groundwork for learning more advanced mathematical concepts.
Strategies for Learning Addition Facts
There are several strategies to help students learn addition facts, including using visual aids, practicing with flashcards, playing math games, and using mnemonic devices. By practicing regularly and applying different strategies, students can improve their recall of addition facts and develop confidence in their math abilities.
Overall, mastering addition facts is an important milestone in a student's mathematical journey and sets the stage for more complex mathematical concepts in the future.
. Create and Print your own Math Worksheetswith Math Worksheet Generator
◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Addition Facts
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key